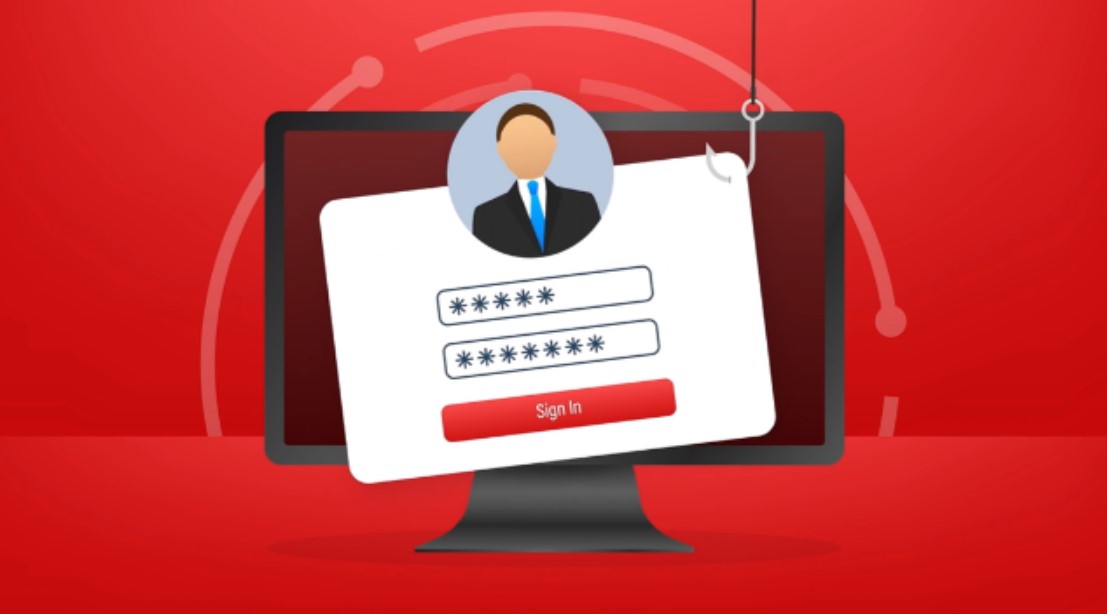

In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is under constant threat. The ability to contain a phishing exploit and stop a ransomware attack in its tracks is paramount. Understanding the nature of these threats and implementing robust defenses is crucial for any cybersecurity administrator.
Phishing Exploits: Clever Deception

Phishing exploits begin with sophisticated deception. Hackers use fraudulent emails or messages to trick users into granting access to their systems. These messages often mimic trusted sources, enticing victims to click malicious links or download infected attachments. Once inside, hackers actively seek vulnerabilities.
Hackers Scanning for Vulnerabilities
Once hackers gain access through phishing, they begin scanning for vulnerabilities within the network. They probe, prying for weak points until they find valuable targets. This could include sensitive data, critical system controls, or other exploitable assets.
Hackers Encrypt Critical Data
Once they find the critical assets, hackers often encrypt valuable data, holding it hostage. This can paralyze businesses, demanding a ransom payment for the decryption key. The inability to access critical data can have devastating consequences.
Examples of Publicized Phishing Exploits
- StrelaStealer Phishing Attacks: In March 2024, the StrelaStealer phishing campaign targeted users by sending emails that appeared to come from trusted organizations. These emails contained links to websites that downloaded malicious software designed to steal credentials and personal information. The attackers moved laterally within compromised networks by scanning for and finding open ports on critical assets, thereby expanding their reach and gathering more data before being detected.
- BlackCat Ransomware Attack (2021): The BlackCat ransomware, also known as ALPHV, targeted organizations worldwide. Hackers used phishing emails to gain initial access to networks and then deployed the ransomware. Once inside, BlackCat not only encrypted critical data but also spread by finding open ports on other machines within the network. This lateral movement allowed BlackCat to maximize damage and increase leverage for ransom demands. The attack was notable for its advanced encryption methods and the high ransoms demanded, causing significant disruption to affected organizations.
Hackers Find Nothing with SSHepherd
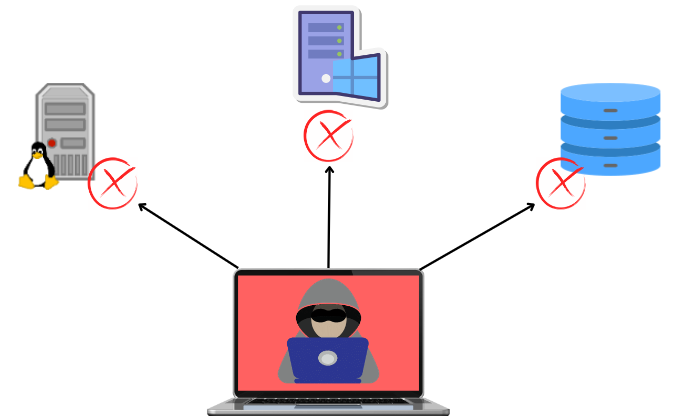
SSHepherd® works by enabling secure connections to your IT resources even while the ports are closed, making them undetectable to hackers. This means that even if a phishing attack is successful for the hacker through an individual machine, they cannot move laterally within your network. They find no open ports to exploit, effectively stopping their attack. SSHepherd® stops movement to critical assets that are protected with SSHepherd®, adding an additional layer of security.
Furthermore, by blocking lateral movement, SSHepherd® gives cybersecurity defenders more time to react to a breach. This extra time can be crucial in identifying and mitigating threats before they cause significant damage.
Proactive Defense: Be Invisible
By making your network stealth, SSHepherd® places you in control. Preventing exploitation is far more effective than reacting to breaches. With SSHepherd®, you can protect your network from the inside out, ensuring that hackers find no vulnerabilities to exploit.
Conclusion
Phishing exploits and ransomware attacks pose significant threats in today’s digital landscape. Implementing SSHepherd® can secure your network against these threats. SSHepherd®’s capability to close open ports and hide them from hacker scans makes your network invisible, providing a robust layer of security.
For more information, please watch our YouTube video on how you can protect your network:
